Keywords:
Retatrutide, Retatrutide’s R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action for Retatrutide, drug target for Retatrutide.
Description:
This article summarized the latest R&D progress of Retatrutide, the Mechanism of Action for Retatrutide, and the drug target R&D trends for Retatrutide.
Text:
Retatrutide‘s R&D Progress
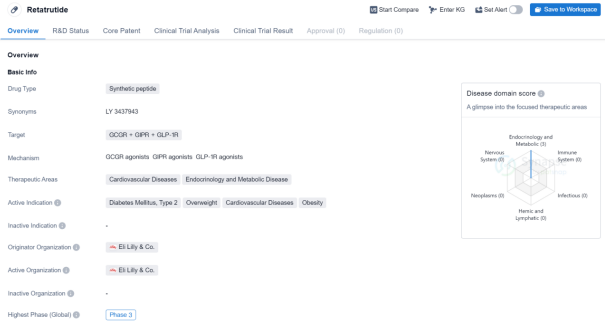
Retatrutide is a synthetic peptide drug that targets three receptors: GCGR, GIPR, and GLP-1R. It falls under the therapeutic areas of cardiovascular diseases, endocrinology, and metabolic diseases. The drug is indicated for the treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2, overweight conditions, cardiovascular diseases, and obesity.
Retatrutide is developed by Eli Lilly & Co., a renowned pharmaceutical organization. Currently, the drug has reached the Phase 3 of clinical development globally.
Being a synthetic peptide, Retatrutide is designed to mimic the actions of natural peptides in the body. By targeting GCGR, GIPR, and GLP-1R receptors, it aims to regulate glucose metabolism, enhance insulin secretion, and promote weight loss. These mechanisms make it a potential candidate for managing diabetes, obesity, and related cardiovascular complications.
The therapeutic areas of cardiovascular diseases, endocrinology, and metabolic diseases are of significant concern globally. Diabetes mellitus type 2, in particular, is a prevalent chronic condition affecting millions of individuals worldwide. The rising prevalence of obesity and associated cardiovascular risks further emphasizes the need for effective treatment options.
Eli Lilly & Co., as the originator organization, has a strong reputation in the pharmaceutical industry. Their expertise and resources contribute to the credibility and potential success of Retatrutide. The drug’s advancement to Phase 3 in both global and Chinese clinical trials indicates promising results in earlier stages.
If Retatrutide successfully completes Phase 3 trials and obtains regulatory approval, it has the potential to address unmet medical needs in the field of diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases. The multi-target approach of targeting GCGR, GIPR, and GLP-1R receptors may provide a comprehensive therapeutic effect, making it a valuable addition to the existing treatment options.
Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for Retatrutide: GCGR agonists, GIPR agonists and GLP-1R agonists
GCGR agonists, GIPR agonists, and GLP-1R agonists are all types of drugs that target specific receptors in the body.
From a biomedical perspective, GCGR agonists are drugs that activate the glucagon receptor (GCGR). The glucagon receptor is found on liver cells and is involved in regulating glucose metabolism. By activating this receptor, GCGR agonists can increase the production and release of glucose from the liver, which can be beneficial in certain medical conditions such as hypoglycemia or diabetes.
GIPR agonists, on the other hand, target the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR). This receptor is primarily found in pancreatic beta cells and plays a role in regulating insulin secretion. GIPR agonists can stimulate the GIPR receptor, leading to increased insulin release and improved glucose control. These drugs are used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
GLP-1R agonists act on the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R), which is also located on pancreatic beta cells. GLP-1R agonists mimic the effects of the hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which is released in response to food intake and helps regulate blood sugar levels. By activating the GLP-1R receptor, these drugs can increase insulin secretion, decrease glucagon release, slow down gastric emptying, and promote satiety. GLP-1R agonists are commonly used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Overall, GCGR agonists, GIPR agonists, and GLP-1R agonists are all drug types that target specific receptors involved in glucose metabolism and insulin regulation. They are used in the management of conditions such as diabetes to help control blood sugar levels and improve overall metabolic health.
Drug Target R&D Trends for Retatrutide
GCGR (Glucagon receptor), GIPR (Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor), and GLP-1R (Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor) play crucial roles in the human body’s glucose metabolism. GCGR regulates glucose production and release from the liver, while GIPR stimulates insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells in response to elevated blood glucose levels. GLP-1R promotes insulin release, inhibits glucagon secretion, slows gastric emptying, and reduces appetite. These receptors collectively contribute to maintaining glucose homeostasis, regulating insulin and glucagon levels, and influencing satiety. Understanding the functions of GCGR, GIPR, and GLP-1R is essential for developing targeted therapies for diabetes and metabolic disorders.
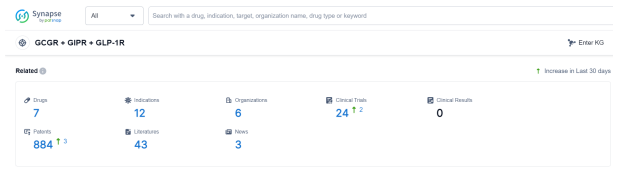
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 26 Sep 2023, there are a total of 7 GCGR + GIPR + GLP-1R drugs worldwide, from 6 organizations, covering 12 indications, and conducting 24 clinical trials.
Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
In conclusion, Retatrutide is a synthetic peptide drug developed by Eli Lilly & Co. It targets GCGR, GIPR, and GLP-1R receptors and shows potential in treating diabetes mellitus type 2, overweight conditions, cardiovascular diseases, and obesity. With its current progress in Phase 3 trials globally, Retatrutide holds promise as a future therapeutic option in the field of biomedicine.